Alberta is one of Canada’s most stunning provinces, known for its breathtaking landscapes, from the majestic Rocky Mountains to vast prairies. Located in Western Canada, Alberta plays a key role in the country’s history and economy. It became a province in 1905 and has since grown into a hub for energy production, agriculture, and tourism.
In this guide, we bring you a guide about Alberta. You’ll discover why the province is a must-visit destination. We’ll explore its natural wonders, vibrant cities like Calgary and Edmonton, and rich cultural heritage. If you are planning a trip or just curious, this guide will give you a clear and exciting overview of what makes Alberta special.
1. History and Culture
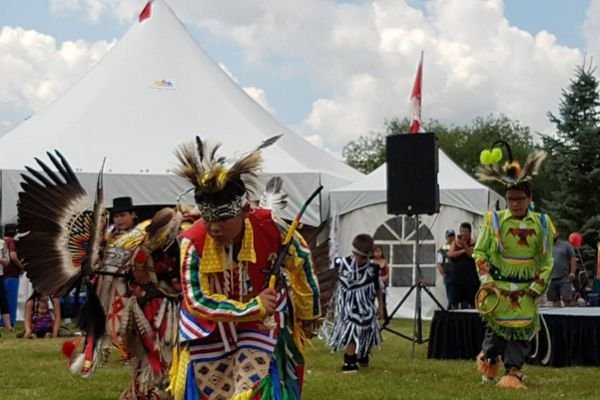

Indigenous Heritage
Alberta’s history begins with its Indigenous peoples, including First Nations and Métis communities. These groups have lived on the land for thousands of years, developing rich cultures and traditions.
Important cultural sites, like the Head-Smashed-In Buffalo Jump, tell the story of how Indigenous peoples used the land for hunting and gathering. This UNESCO World Heritage site is one of the oldest, best-preserved buffalo jumps in the world.
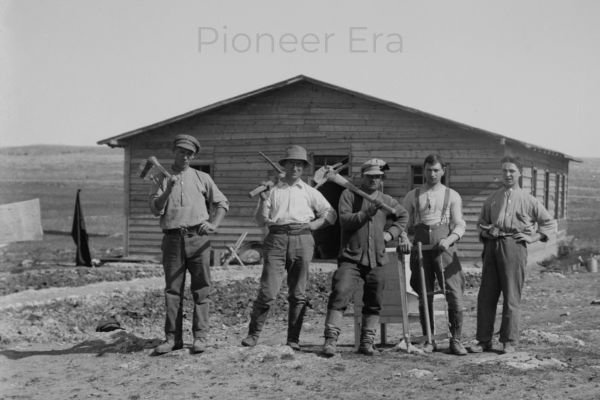

The Pioneer Era
The Pioneer Era marks the arrival of European settlers in Alberta. During the 19th century, fur traders and ranchers began to explore and settle in the region.
The fur trade played a crucial role in Alberta’s early economy, with trading posts becoming the first European settlements. Ranching soon followed as the vast prairies provided ideal conditions for raising cattle. These early industries laid the foundation for Alberta’s growth as a province.
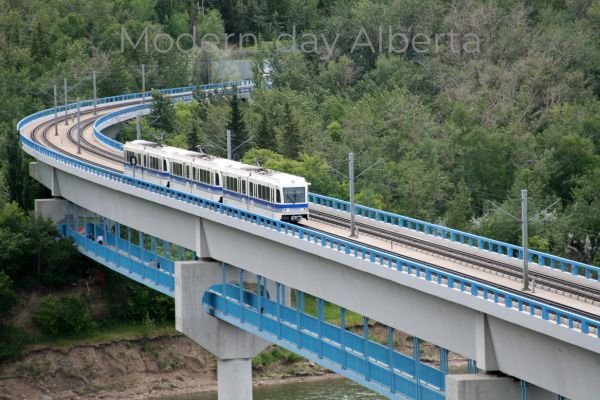

Modern-day Alberta
Today, Alberta is known for its rapidly growing cities and strong economy. Calgary and Edmonton, where I currently live, have become major urban centers with vibrant cultures and diverse populations.
Alberta plays a significant role in Canada’s economy, especially in energy production, agriculture, and technology. The province’s modern history is one of growth, innovation, and cultural diversity, making it a dynamic place to live and visit.
2. First Nations in Alberta
Overview of First Nations
Alberta is home to a diverse and vibrant Indigenous population, with more than 258,000 First Nations, Métis, and Inuit people living in the province. There are 48 distinct First Nations in Alberta, divided into three major cultural groups: the Plains Cree, the Dene, and the Blackfoot. These groups have lived on the land for thousands of years, developing rich cultures, languages, and traditions that continue to thrive today.
Treaty Areas
Alberta is covered by several historic treaties between the Canadian government and Indigenous peoples. The most significant of these are Treaty 6, Treaty 7, and Treaty 8, which were signed in the late 19th century. These treaties were meant to define the relationship between the First Nations and the Crown, including land use and rights. Today, these treaties remain important documents that continue to influence the relationship between Indigenous peoples and the Canadian government. Understanding these treaties is key to recognizing the rights and sovereignty of First Nations in Alberta.
Cultural Heritage and Traditions
The First Nations in Alberta have a rich cultural heritage that is deeply connected to the land. Traditional practices such as hunting, fishing, and gathering continue to be important aspects of life for many Indigenous people. The spiritual connection to the land is reflected in ceremonies like the Sun Dance, which is still practiced today. The preservation of Indigenous languages, such as Cree and Blackfoot, is also a priority for many First Nations communities, as language is a vital part of cultural identity.
Contributions to Alberta
First Nations have made and continue to make significant contributions to the cultural, economic, and social fabric of Alberta. Indigenous businesses are growing across the province, contributing to sectors such as tourism, arts, and resource management. Events like the Calgary Stampede and Edmonton’s Indigenous Peoples Festival celebrate Indigenous culture, offering opportunities for both Indigenous and non-Indigenous people to learn and appreciate this rich heritage.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their resilience and contributions, First Nations in Alberta face ongoing challenges, including issues related to land rights, health disparities, and economic opportunities. Efforts are being made to address these challenges through initiatives focused on education, economic development, and reconciliation. The Truth and Reconciliation Commission’s calls to action have prompted many organizations and governments in Alberta to work towards better relationships with Indigenous communities and to honor their rights and contributions.
3. Geography and Natural Beauty

Alberta's Landscape
Alberta is one of Canada’s most geographically diverse provinces, spanning over 661,000 square kilometres. The province is home to a variety of landscapes, including the towering Rocky Mountains, vast prairies, rugged badlands, and dense boreal forests.
These different regions offer a wide range of natural beauty and are a major draw for tourists. Alberta’s diverse ecosystems support a rich array of wildlife and provide countless opportunities for outdoor activities year-round.

The Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains in Alberta are among Canada’s most iconic natural wonders. Banff and Jasper National Parks, both UNESCO World Heritage sites, draw millions of visitors each year.
Banff, established in 1885, is Canada’s oldest national park, while Jasper is the largest in the Rockies. Together, they showcase stunning peaks like Mount Assiniboine and Mount Robson — the tallest at 3,954 meters.
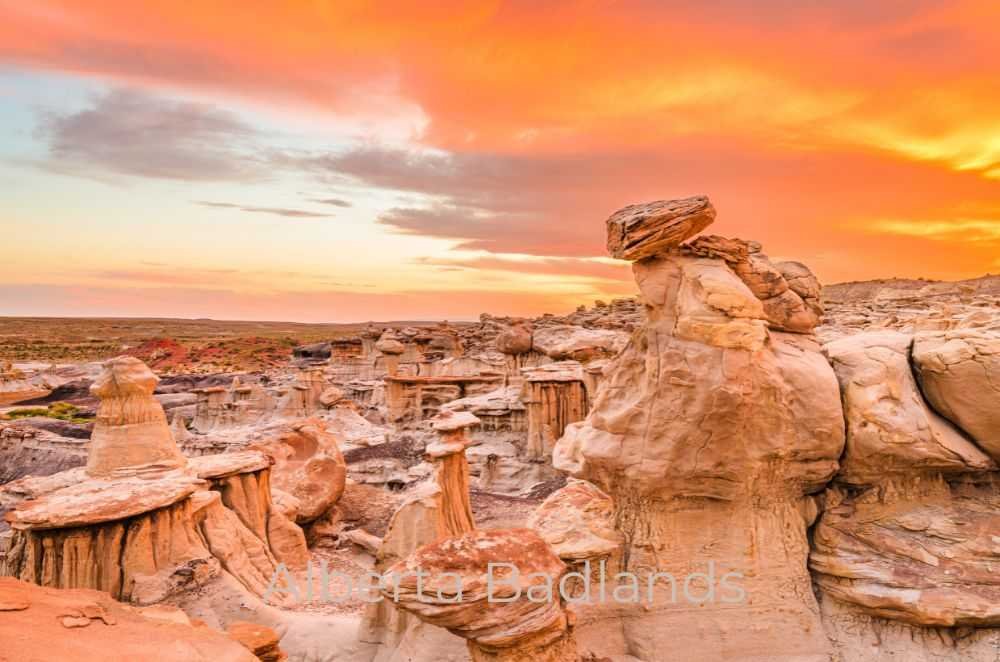

The Badlands
The Alberta Badlands, located in southeastern Alberta, are famous for their striking landscapes and rich fossil beds.
The Drumheller region, known as the “Dinosaur Capital of the World,” has produced some of the most important fossil discoveries. Nearby Dinosaur Provincial Park, a UNESCO World Heritage site, has yielded over 150 complete dinosaur skeletons since its founding.
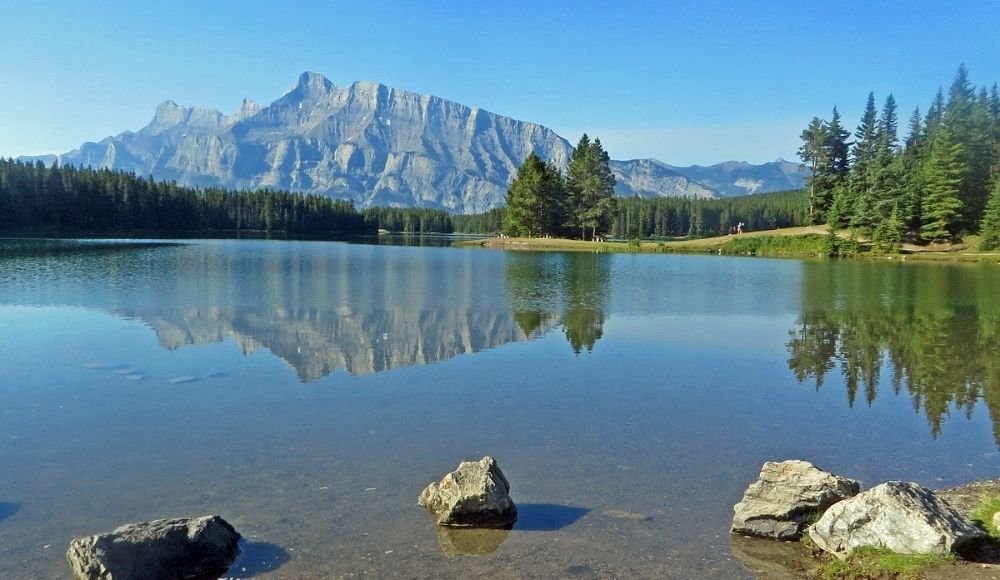

Lakes & Rivers
Alberta’s Rocky Mountains feature some of Canada’s most stunning lakes and rivers. Lake Louise, Peyto Lake, and Moraine Lake are famous for their turquoise hues created by glacial silt, attracting millions to Banff National Park each year.
The 1,231-kilometre Athabasca River supports diverse ecosystems, while the Bow River, flowing through Calgary, provides water and recreation like fishing, kayaking, and rafting.

The Prairies
Alberta’s southern and central regions are dominated by vast prairies with rich soil, forming one of Canada’s key agricultural zones. The region produces major crops like wheat, canola, and barley — accounting for about 32% of Canada’s total wheat output in 2022.
These open landscapes also support wildlife such as deer, coyotes, and many bird species, making the prairies both productive and scenic.

Population and Language
Alberta is home to over 4.5 million people (2023), making it Canada’s fourth most populous province.
English is the main language used in daily life, but around 20% of residents speak another language at home — including Tagalog, Punjabi, Spanish, and French. The province also has a strong Indigenous presence, where Cree, Blackfoot, and Dene are still spoken in First Nations communities.
4. Major Cities and Urban Life
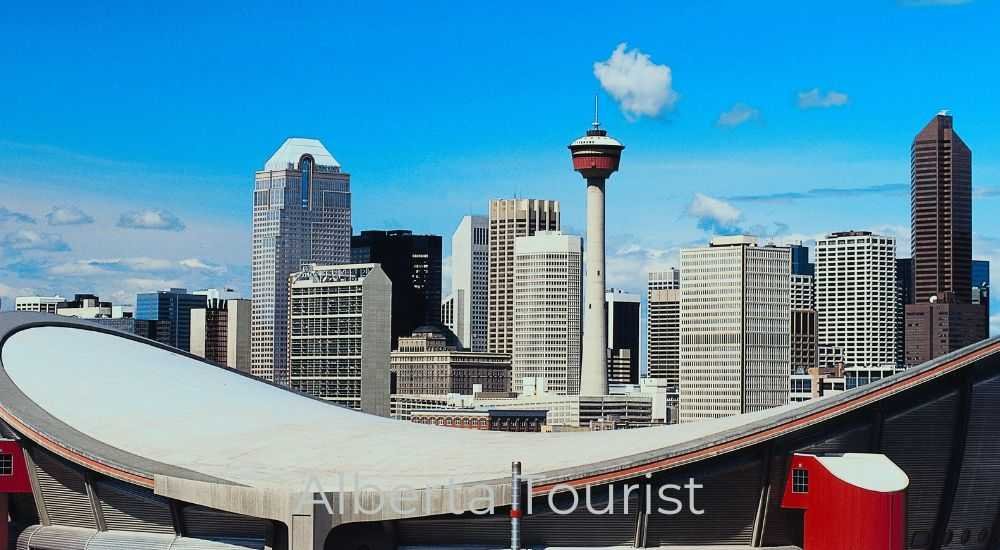

Calgary
Calgary, Alberta’s largest city with over 1.3 million residents, is a major economic hub driven by the oil and gas industry, finance, and technology. Known for its Western heritage, Calgary hosts the annual Calgary Stampede, attracting over a million visitors.
The city’s skyline features the iconic Calgary Tower, offering panoramic views of the Rockies. Calgary’s cultural scene includes the Glenbow Museum and the Calgary Philharmonic Orchestra.

Edmonton
Edmonton isAlberta’s capital. The city has about 1 million residents and a diverse economy focused on government, education, and technology. Known as the “Gateway to the North,” Edmonton features the North Saskatchewan River Valley, the largest urban parkland in North America.
The city’s key attractions include West Edmonton Mall, the largest shopping mall in North America, and the Alberta Legislature. Edmonton is also famous for its festivals, earning the nickname “Festival City.”

Other Notable Cities
Red Deer (population: 103,000) is centrally located between Calgary and Edmonton, known for agriculture and oil services. Lethbridge (population: 101,000) thrives on agriculture and hosts the University of Lethbridge.
Medicine Hat (population: 65,000), known as “The Gas City,” boasts a sunny climate, a historic downtown, and proximity to the Badlands.
5. Alberta’s Economy and Industry

The Oil & Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry is the backbone of Alberta’s economy, contributing about 27% to the province’s GDP. Alberta is home to the third-largest oil reserves in the world, following Saudi Arabia and Venezuela.
The province’s key oil sands projects, located in the Athabasca, Cold Lake, and Peace River regions, produce over 3 million barrels of oil per day. The oil sands are a crucial part of Alberta’s economy, providing jobs to thousands of people and generating billions in revenue. Companies like Suncor Energy, Canadian Natural Resources, and Imperial Oil are major players in this sector, driving economic growth and investment in the region.

Agriculture & Farming
Agriculture is another vital sector in Alberta, contributing around 2.2% to the provincial GDP. The province has over 50,000 farms, covering more than 50 million acres of farmland.
Alberta is one of Canada’s leading producers of beef, accounting for nearly 40% of the country’s beef production. Wheat, canola, and barley are the major crops grown in Alberta, with the province being a significant contributor to Canada’s grain exports. Livestock farming, particularly cattle, plays a significant role, with over 5 million head of cattle being raised in the province. Agriculture not only supports the economy but also helps sustain rural communities across Alberta.

Tourism in Alberta
Tourism is a growing industry in Alberta, contributing approximately $8.2 billion to the economy annually. The province attracts millions of visitors each year, drawn by its stunning natural landscapes, vibrant cities, and cultural heritage. Major attractions like Banff and Jasper National Parks, the Calgary Stampede, and West Edmonton Mall are key drivers of tourism.
In 2019, Alberta welcomed over 36 million visitors, with international travelers making up a significant portion. Events like the Edmonton Folk Music Festival and Calgary’s Global Fest also play a crucial role in boosting tourism. The industry supports over 127,000 jobs, making it a vital part of Alberta’s diverse economy.
6. Alberta’s Natural Wonders and Outdoor Activities

National & Provincial Parks
Alberta’s natural beauty is protected across 75 provincial and 5 national parks, making it a haven for outdoor enthusiasts. Banff, founded in 1885, is the oldest and most famous, while Jasper, the largest in the Rockies, spans over 11,000 square kilometres.
Waterton Lakes, where prairies meet mountains, and parks like Elk Island and Wood Buffalo showcase Alberta’s incredible mix of mountains, lakes, and forests.

Outdoor Activities in Alberta
Alberta is an outdoor lover’s paradise, offering adventures year-round. Banff National Park alone has over 1,000 km of hiking trails, while the province boasts 500+ campgrounds in scenic spots like Kananaskis and the Icefields Parkway.
In winter, top resorts such as Lake Louise and Sunshine Village draw skiers and snowboarders. Alberta also offers great fishing, canoeing, biking, and wildlife photography.

Wildlife in Alberta
Alberta is a wildlife haven, home to grizzly bears, black bears, moose, and wolves. Jasper National Park alone hosts over 53 mammal species, while Banff is known for elk, deer, and bighorn sheep.
The province also shelters 400+ bird species, including bald eagles and great horned owls. With more than 580 protected areas, Alberta offers endless chances to experience wildlife in its natural habitat.
7. Unique Attractions and Hidden Gems
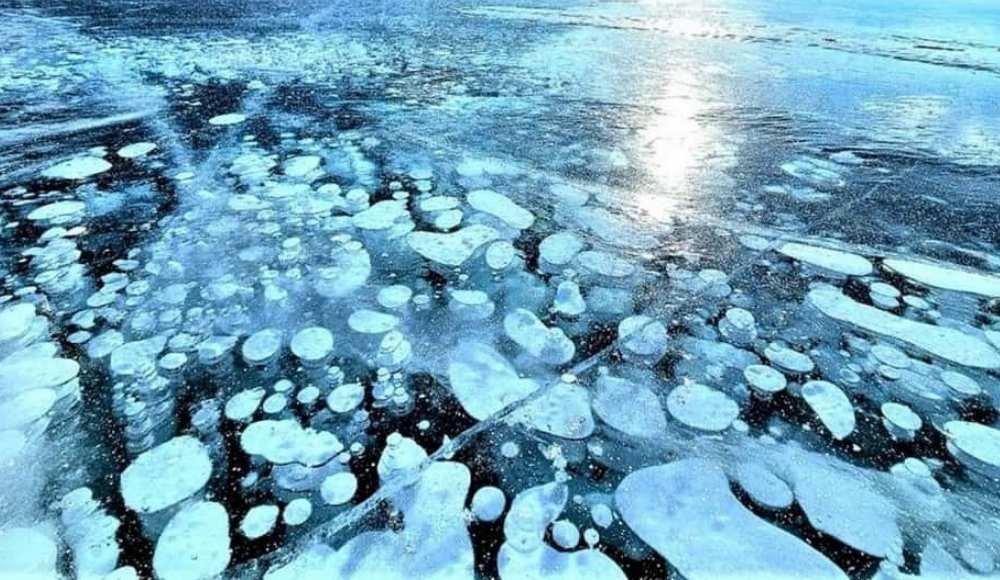

Unpopular Natural Sites
While Alberta is famous for its iconic sites like Banff and Jasper, the province also offers some incredible lesser-known natural attractions. Abraham Lake, located in the Kootenay Plains, is a stunning man-made lake known for its frozen methane bubbles that create an otherworldly sight during winter.
Another hidden gem is Dinosaur Provincial Park, a UNESCO World Heritage site. Located in the Badlands, this park is one of the richest fossil beds in the world, with over 50 dinosaur species discovered here.

Cultural Attractions
Alberta offers more than natural beauty — it’s rich in culture too. The Royal Tyrrell Museum in Drumheller houses one of the world’s largest dinosaur fossil collections, while Calgary’s Glenbow Museum explores Western Canada’s history and art.
Alberta is also home to numerous festivals, such as the Calgary Folk Music Festival and Edmonton’s Fringe Theatre Festival, the latter being the second-largest fringe festival in the world. These cultural attractions showcase Alberta’s vibrant arts and history.

Stargazing & Northern Lights
Alberta is one of Canada’s top stargazing destinations, with vast open skies and low light pollution. The Jasper Dark Sky Preserve, one of five in the province, offers incredible views of stars, planets, and the Northern Lights. Each October, it hosts the Jasper Dark Sky Festival, drawing visitors worldwide.
Other top spots include Elk Island and Waterton Lakes National Parks, where the Milky Way lights up the sky.
Read my post about the best places to witness Northern Lights in Alberta
8. How to get to Alberta

By Air
The most convenient way to reach Alberta is by air. Alberta has two major international airports: Calgary International Airport (YYC) and Edmonton International Airport (YEG).
Both airports offer direct flights from major cities across Canada, the United States, Europe, and Asia.
Calgary International Airport is the busiest in Alberta, handling over 18 million passengers annually, making it a popular entry point for visitors heading to the Rocky Mountains. Edmonton International Airport serves around 8 million passengers a year and is well-connected to both domestic and international destinations.

By Road
If you’re travelling from neighbouring provinces or the United States, driving to Alberta is a scenic and flexible option. Major highways, such as the Trans-Canada Highway (Highway 1) and the Queen Elizabeth II Highway (Highway 2), provide easy access to the province.
The drive from Vancouver, British Columbia, to Calgary takes about 10 hours and offers breathtaking views of the Rocky Mountains along the way. From the United States, Interstate 15 connects to Alberta through Montana, leading to cities like Lethbridge and Calgary.

By Train
For a more leisurely and scenic journey, consider traveling to Alberta by train. VIA Rail offers routes that connect Alberta to other parts of Canada, including the popular “Canadian” route that runs from Vancouver to Toronto, passing through Jasper National Park.
The Rocky Mountaineer is another famous train service, offering luxury rail journeys through the Rockies, with stops in Banff, Lake Louise, and Jasper.
Entering Alberta through US-Canada Borders
If you’re travelling to Alberta from the United States, several border crossings provide entry into the province. Each of these border crossings offers a unique route into Alberta, depending on your starting point and destination.
- Carway Border: Located on Highway 2, the Carway Border connects Alberta with Montana and is a convenient entry point for travelers heading to southern Alberta, including popular destinations like Waterton Lakes National Park.
- Del Bonita Border: This border crossing on Highway 62 offers a quieter route into Alberta, primarily used by those traveling to the central part of the province, including Lethbridge and the surrounding agricultural areas.
- Sweet Grass Border: The Sweet Grass Border, connected by Interstate 15 in Montana and Highway 4 in Alberta, is one of the busiest crossings and is ideal for those traveling to Lethbridge or continuing to Calgary.
- Aden Border: Located on Highway 880, the Aden Border is a lesser-used crossing that serves travelers heading to the southeastern regions of Alberta, including Medicine Hat.
- Wild Horse Border: This crossing on Highway 41 is perfect for those seeking a scenic route into southeastern Alberta, offering access to the prairies and Badlands, including the Dinosaur Provincial Park area.
10. Alberta Travel Tips and Recommendations
Best Time to Visit Alberta
Alberta is a year-round destination, with each season offering its own unique experiences. The best time to visit depends on what you want to do. Summer (June to August) is the most popular time for outdoor activities like hiking, camping, and exploring national parks. The weather is warm, with average temperatures ranging from 15°C to 35°C.
Fall (September to November) is perfect for witnessing the stunning fall foliage, especially in the Rocky Mountains. Winter (December to February) transforms Alberta into a winter wonderland, ideal for skiing, snowboarding, and ice skating. Average temperatures in winter range from -5°C to -35°C, so it’s important to dress warmly. Spring (March to May) brings mild weather and fewer crowds, making it a great time to visit before the summer rush.3
Getting Around
Alberta is a vast province, so having a plan for getting around is essential. Renting a car is the most convenient option, especially if you plan to explore the national parks and rural areas. Alberta has well-maintained highways, and driving gives you the flexibility to stop at various attractions along the way.
Road trips are popular, with routes like the Icefields Parkway offering some of the most scenic drives in the world. Public transit is available in major cities like Calgary and Edmonton, with buses and light rail systems providing easy access to urban attractions. For longer distances, flights between cities or train travel via VIA Rail can also be considered.
Where to Stay in Alberta
Alberta offers a wide range of accommodations to suit different preferences and budgets. In the cities, you’ll find everything from luxury hotels to budget-friendly motels. Calgary and Edmonton have a variety of options, including well-known hotel chains and boutique hotels.
For a more unique experience, consider staying at a mountain lodge or resort in places like Banff or Jasper, where you can enjoy stunning views and easy access to outdoor activities. Campgrounds are plentiful in Alberta’s national and provincial parks, with options ranging from basic tent sites to fully-equipped RV spots. Camping is a popular choice for those looking to immerse themselves in nature.
What to Park
What you pack for your trip to Alberta depends on the season and the activities you plan to do. In summer, bring lightweight clothing, a good pair of hiking boots, sunscreen, and a hat for sun protection. Even in summer, the weather can be unpredictable, so it’s wise to pack a waterproof jacket and layers for cooler evenings.
For winter visits, pack warm clothing, including thermal layers, a heavy coat, gloves, a scarf, and insulated boots. If you plan to ski or snowboard, don’t forget your gear or consider renting equipment locally. Regardless of the season, always pack a reusable water bottle, as staying hydrated is important when exploring Alberta’s natural landscapes.
Conclusion: Things to know about Alberta
Alberta is a province like no other, offering a unique blend of stunning natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and vibrant urban life. From the majestic Rocky Mountains and expansive prairies to the historical significance of its Indigenous communities and the bustling energy of cities like Calgary and Edmonton, Alberta will wow you.
We encourage you to explore all that Alberta has to offer. Discover its hidden gems, immerse yourself in the local culture, and take in the breathtaking scenery that makes this province so special. Alberta’s natural wonders and diverse attractions are waiting for you to experience them firsthand.
If you’ve visited Alberta or are planning a trip, we’d love to hear about your experiences. Feel free to share your stories, ask questions, or leave comments. Your insights can help others discover the magic of Alberta and make the most of their visit.
Alberta FAQs
Alberta is best known for its stunning Rocky Mountains, including Banff and Jasper National Parks, and its role as a leader in Canada’s oil and gas industry.
Alberta’s unique mix of breathtaking natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and economic vitality make it a special place to live and visit..
Alberta is known for its high-quality beef, especially Alberta steak, and its production of wheat and canola.
Alberta is rich in natural resources, particularly oil and gas, as well as fertile farmland for agriculture.
Alberta’s main animal is the bison, which is also the provincial symbol.